


Jul 29, 2025
-
By Clive

![]() AI Summary By Kroolo
AI Summary By Kroolo
In today's fast-paced software development landscape, effective sprint planning has become the cornerstone of successful project delivery. Organizations worldwide are discovering that structured sprint planning not only accelerates development cycles but also ensures teams remain aligned, focused, and productive throughout their journey.
Whether you're a seasoned project manager or new to agile methodologies, understanding the intricacies of sprint planning can transform how your team approaches complex projects and delivers value to stakeholders.
 Sprint planning is a collaborative ceremony within the Scrum framework where development teams define what work will be accomplished during an upcoming sprint and determine how that work will be achieved.
Sprint planning is a collaborative ceremony within the Scrum framework where development teams define what work will be accomplished during an upcoming sprint and determine how that work will be achieved.
This crucial meeting brings together the product owner, scrum master, and development team to establish clear objectives, prioritize backlog items, and create a shared understanding of the sprint's goals.
At its core, sprint planning represents a systematic approach to breaking down complex projects into manageable, time-boxed iterations called sprints. These sprints typically last between one to four weeks, with most organizations favoring two-week cycles for optimal balance between planning overhead and delivery frequency.
The primary purpose is to select the right set of product backlog items to work on during the sprint and discuss each item enough to feel confident beginning work.
Every successful sprint planning session revolves around three fundamental elements: establishing a sprint goal, understanding team capacity, and creating a prioritized set of backlog items.
The sprint goal serves as the north star, providing direction and purpose for the entire team throughout the iteration. Team capacity assessment ensures realistic commitments based on available resources, skill sets, and potential constraints.
The sprint planning process involves collaborative decision-making where team members actively participate in selecting work items and estimating effort required for completion. During these sessions, teams review the product backlog, discuss technical requirements, identify dependencies, and commit to deliverable outcomes. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone understands expectations and feels ownership over their commitments.
Unlike traditional waterfall planning approaches, sprint planning embraces adaptability and iterative improvement. While conventional methods often require extensive upfront planning with limited flexibility for changes, sprint planning acknowledges uncertainty and builds adaptation mechanisms into the development process.
This approach allows teams to respond quickly to changing requirements while maintaining progress toward larger objectives.
Three key roles participate in sprint planning: the product owner who defines priorities and acceptance criteria, the scrum master who facilitates the process and removes impediments, and the development team who estimates work and commits to deliverables.
Each role brings unique perspectives and responsibilities that contribute to comprehensive planning outcomes.
The primary artifacts produced during sprint planning include the sprint goal, sprint backlog, and task assignments with time estimates. These artifacts serve as reference points throughout the sprint, helping teams maintain focus and track progress toward established objectives.
The sprint backlog becomes the definitive source of truth for what work will be completed during the iteration.

Effective sprint planning serves as the foundation for successful agile project delivery, providing teams with structure, clarity, and purpose that drive exceptional results.
Organizations that invest in robust sprint planning processes consistently report higher team productivity, improved stakeholder satisfaction, and better alignment between development efforts and business objectives.
Sprint planning creates a shared understanding among team members about priorities, goals, and expectations for the upcoming iteration. This alignment eliminates confusion, reduces conflicting priorities, and ensures everyone works toward common objectives.
When teams have crystal-clear direction, they can dedicate their energy to productive work rather than navigating ambiguity or resolving misunderstandings.
Through systematic planning for sprint execution, teams develop reliable velocity patterns that enable more accurate forecasting of future deliverables. Historical sprint data provides valuable insights into team capabilities, helping organizations make informed commitments to stakeholders and plan release schedules with greater confidence.
This predictability builds trust between development teams and business stakeholders.
Sprint planning sessions provide opportunities to identify potential obstacles, dependencies, and risks before they impact development progress. Teams can proactively address challenges, plan mitigation strategies, and allocate resources appropriately.
This early risk identification prevents costly delays and ensures smoother sprint execution with fewer surprises.
Regular sprint planning cycles create natural checkpoints for teams to reflect on their processes, identify improvement opportunities, and implement changes incrementally.
This iterative approach to process enhancement helps teams become more efficient over time while maintaining high quality standards. Each planning session builds upon lessons learned from previous sprints.
Sprint planning provides structured opportunities for stakeholder input and feedback, ensuring that development efforts remain aligned with business needs and customer expectations. Regular planning cycles create transparency into team progress, capacity constraints, and delivery timelines. This visibility helps stakeholders make informed decisions and adjust priorities as needed.
Through careful planning for sprint activities, organizations can optimize resource allocation, balance workloads across team members, and identify capacity constraints before they become bottlenecks. This proactive approach to resource management ensures that teams operate at a sustainable pace while maximizing productivity and maintaining work quality standards.
The concept of sprint planning emerged from the broader Scrum methodology, which revolutionized software development by introducing iterative, collaborative approaches to project management. Understanding this historical context provides valuable insights into why sprint planning has become such a fundamental practice in modern agile development.
The term "scrum" originated from a 1986 Harvard Business Review paper titled "The New New Product Development Game" by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka.
The authors observed successful product development teams in automotive, photocopier, and printer industries and noted their resemblance to rugby teams - cross-functional units working together to advance toward a common goal through collaborative effort and continuous adaptation.
In the early 1990s, Ken Schwaber implemented what would become scrum principles at Advanced Development Methods, while Jeff Sutherland developed similar approaches at Easel Corporation.
Their independent work on iterative development processes eventually converged into the formal Scrum framework. Sutherland and Schwaber collaborated to integrate their ideas, testing and refining the methodology through practical application.
The publication of the Agile Manifesto in 2001 marked a pivotal moment for sprint planning and Scrum methodology. This document established core principles that emphasized individuals and interactions over processes and tools, working software over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, and responding to change over following a plan. These principles directly influenced how sprint planning evolved.
Ken Schwaber founded the Scrum Alliance in 2002 and established the Certified Scrum accreditation series, providing formal training and certification programs for practitioners. Later, Schwaber left to found Scrum.org, creating parallel Professional Scrum certifications. These initiatives helped standardize sprint planning practices and establish consistent methodologies across organizations worldwide.
Since 2009, "The Scrum Guide" has served as the definitive resource for Scrum practices, including sprint planning methodologies. Written by Schwaber and Sutherland, this document has been revised six times, with the most recent version published in November 2020. Each revision reflects accumulated knowledge and best practices from global Scrum implementations.
Contemporary sprint planning has evolved beyond its original software development roots to encompass diverse industries and project types. Modern practices incorporate advanced estimation techniques, digital collaboration tools, and data-driven decision making while maintaining the collaborative, adaptive spirit of the original methodology. This evolution continues as organizations discover new applications for sprint-based project management approaches.
Implementing systematic sprint planning delivers measurable benefits that extend far beyond simple task organization. Organizations that embrace comprehensive sprint planning methodologies consistently experience improved team dynamics, enhanced product quality, and superior stakeholder satisfaction across their development initiatives.
Sprint planning establishes dedicated review periods where stakeholders assess deliverables, provide feedback, and ensure quality standards are maintained. Development teams utilize insights from sprint retrospectives to iterate and improve functionality continuously.
This ongoing adaptation cycle enhances software development quality in future sprints while building a culture of excellence and continuous learning.
By concentrating on specific user stories within a sprint backlog, team members can focus on one priority at a time without distraction. The sprint planning process ensures clarity and purpose, significantly improving productivity by aligning team efforts with sprint goals.
This focused approach eliminates context switching and allows developers to achieve deep work states that maximize output quality.
Sprint planning helps organizations manage resources efficiently, even when client requirements change unexpectedly. Teams can adjust upcoming sprints without disrupting deliverables from previous iterations, leading to significant cost savings throughout the product development lifecycle.
This agility prevents waste and ensures optimal utilization of development resources.
Agile teams thrive on teamwork and communication fostered through regular sprint planning sessions. Scrum events including daily scrums, sprint reviews, and sprint retrospectives promote collaboration between product owners, scrum masters, and team members.
Regular planning meetings encourage knowledge sharing and improve overall team effectiveness through enhanced communication patterns.
Daily scrums and sprint planning help identify potential issues early, allowing teams to develop solutions before problems escalate into major obstacles. Frequent feedback loops within each iteration enable teams to resolve dependencies and adapt sprint goals when circumstances change. This proactive risk management approach ensures stable progress throughout sprint cycles.
Management tools integrated with sprint planning provide all team members visibility into user story progress and task completion status. Product backlogs, sprint backlogs, and burndown charts offer clear insights into work completed and remaining effort required.
This transparency keeps everyone aligned with overall product goals while ensuring accountability within established workflows and processes.
Kroolo emerges as a comprehensive solution for teams seeking to optimize their sprint planning processes through integrated project management capabilities.
This innovative platform combines traditional sprint planning functionalities with modern collaboration tools, creating an environment where teams can plan, execute, and monitor their sprints with unprecedented efficiency and clarity.
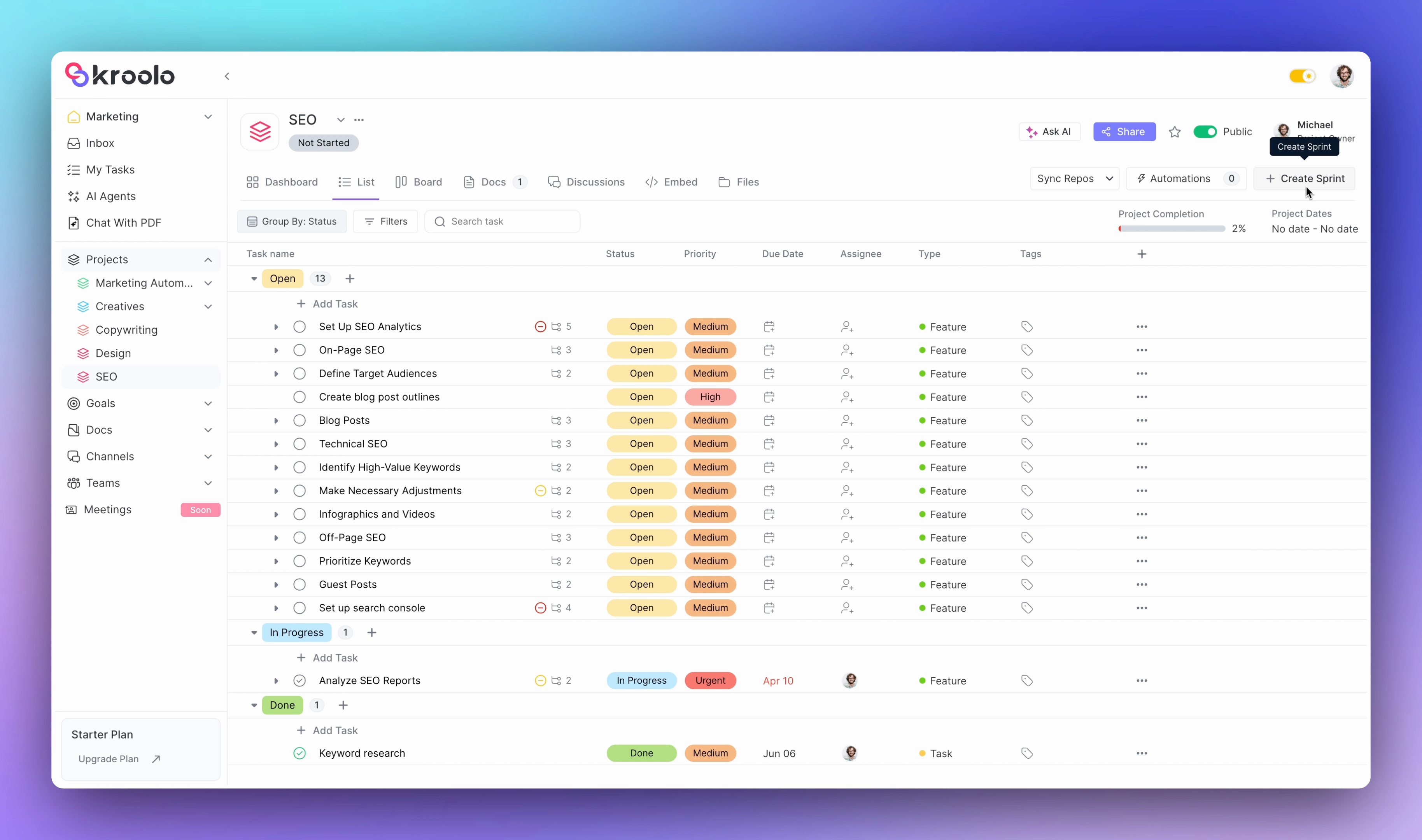
Kroolo simplifies the sprint creation process through an intuitive interface that guides users through essential setup steps. Teams can easily navigate to their project section, create new sprints with customized names and durations, and set specific start and completion dates. The platform allows teams to exclude non-working days from sprint calculations, ensuring realistic timeline planning that accounts for holidays and organizational schedules.
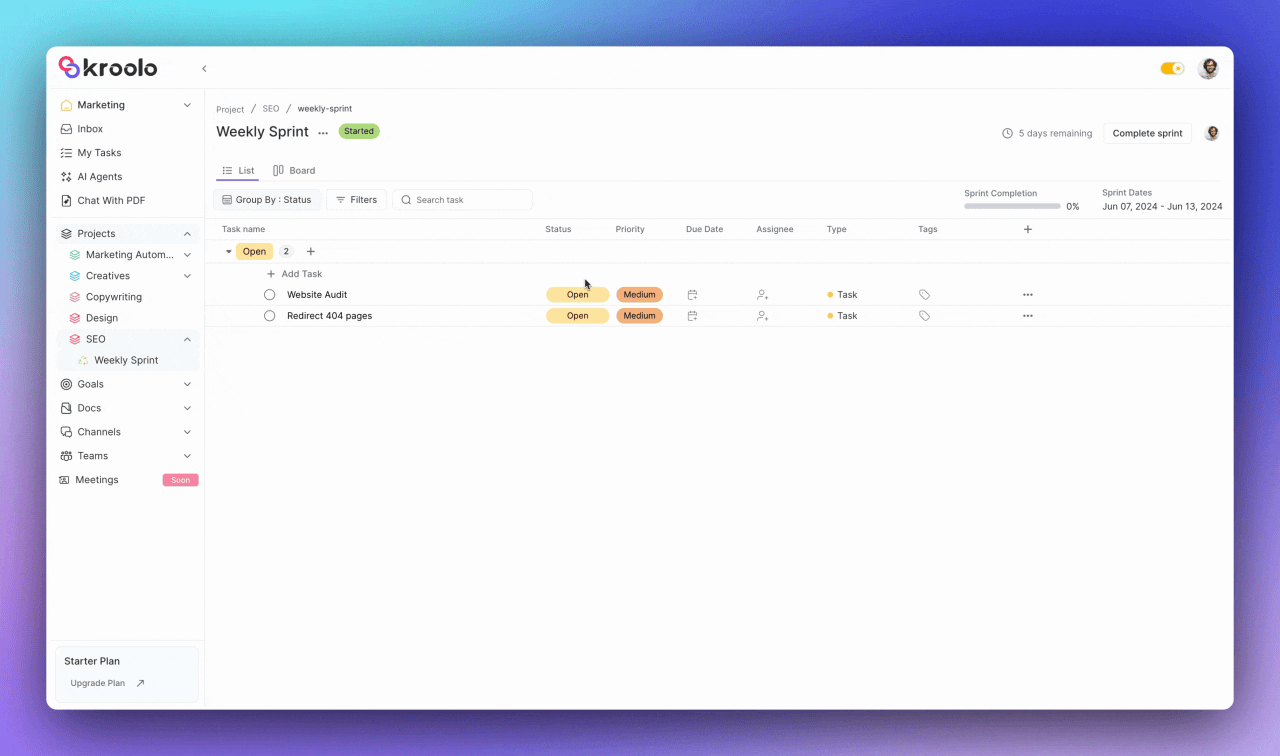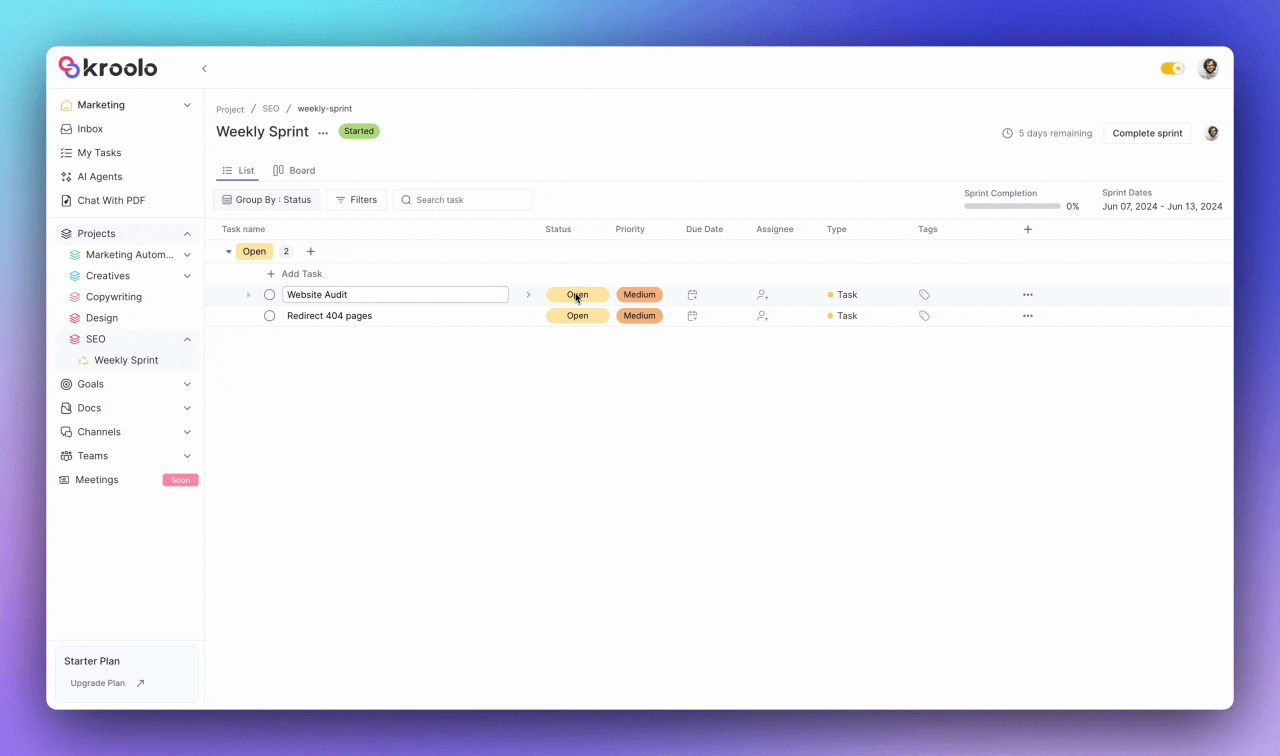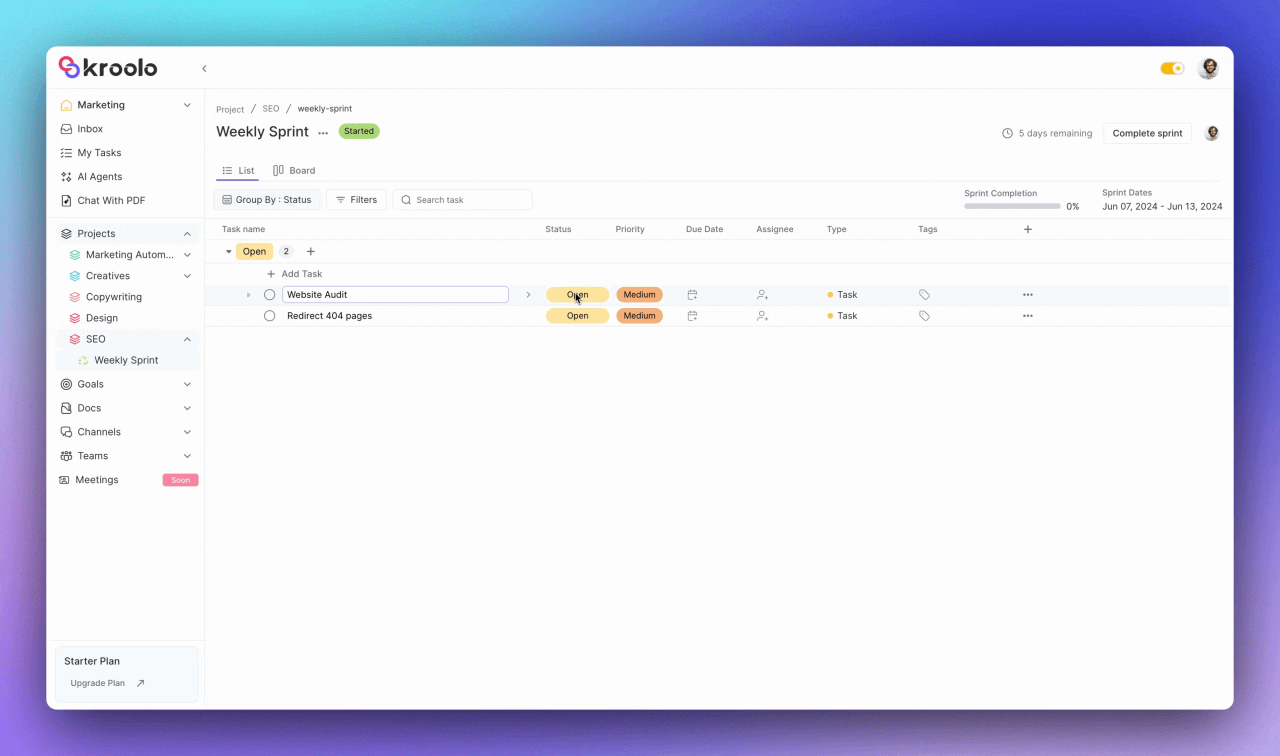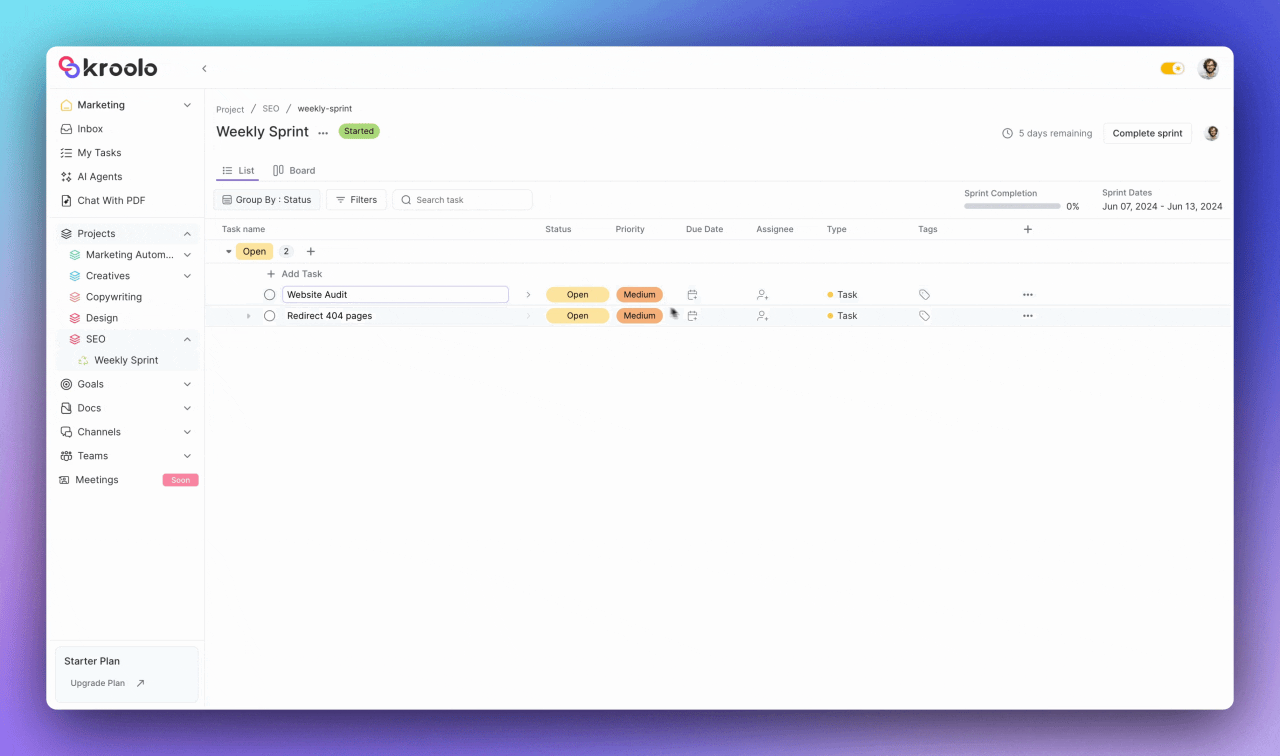
The platform excels in task organization capabilities, allowing teams to add, modify, and manage tasks within their sprints effectively.
Users can adjust task details including status, priority, due date, and assignee information while adding estimated and actual story points for accurate capacity planning. The system supports task categorization through relevant tags and provides flexible column customization options.
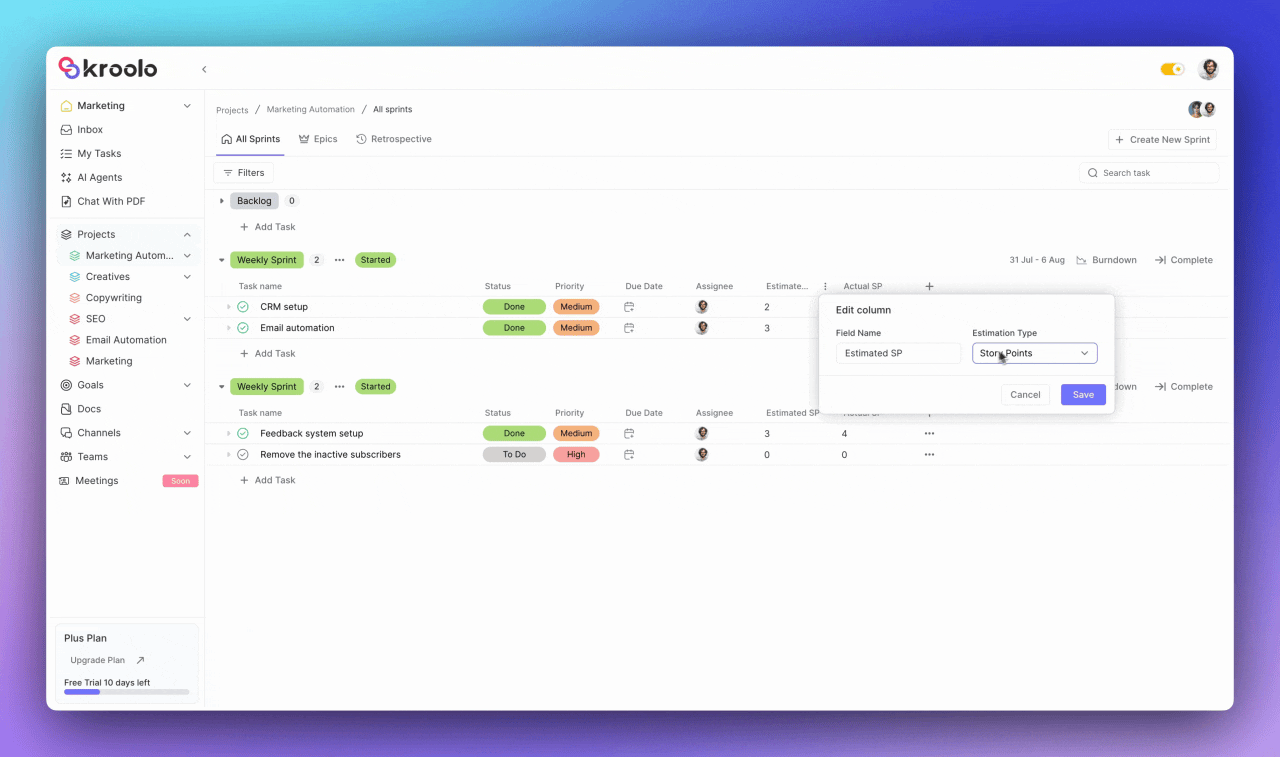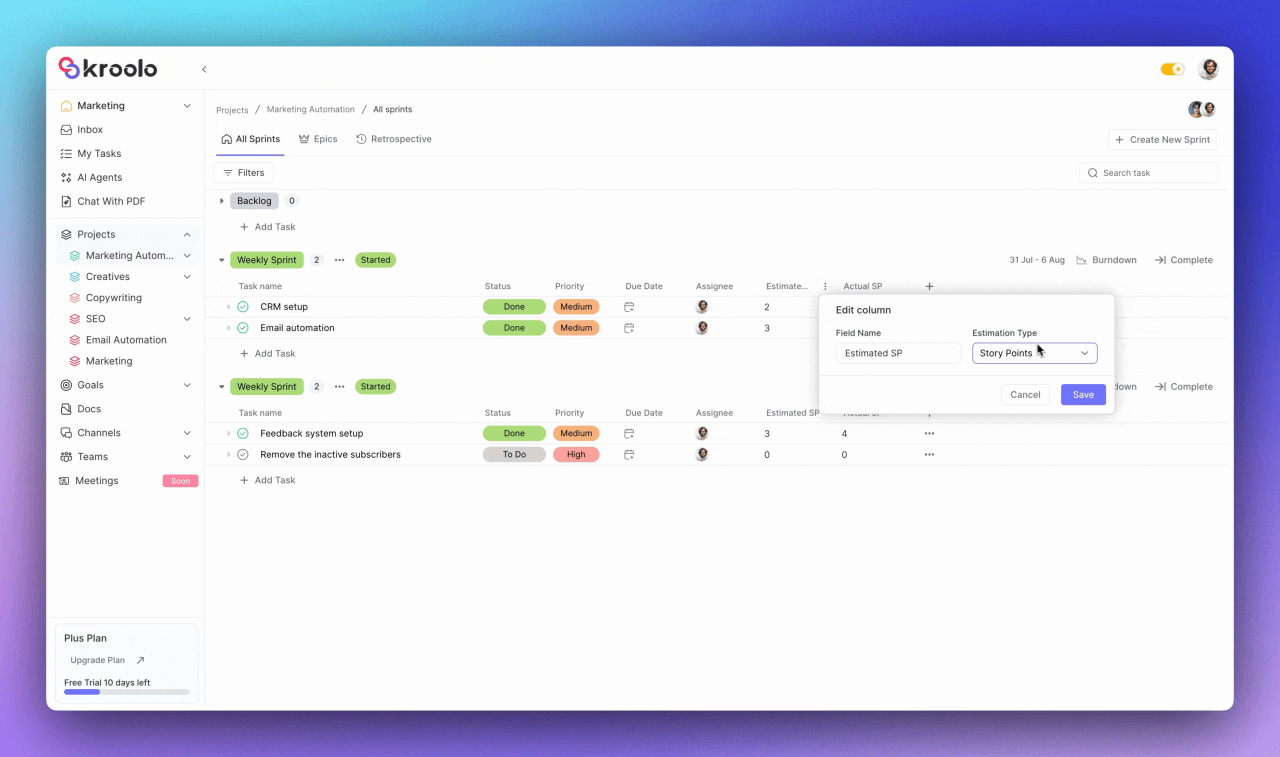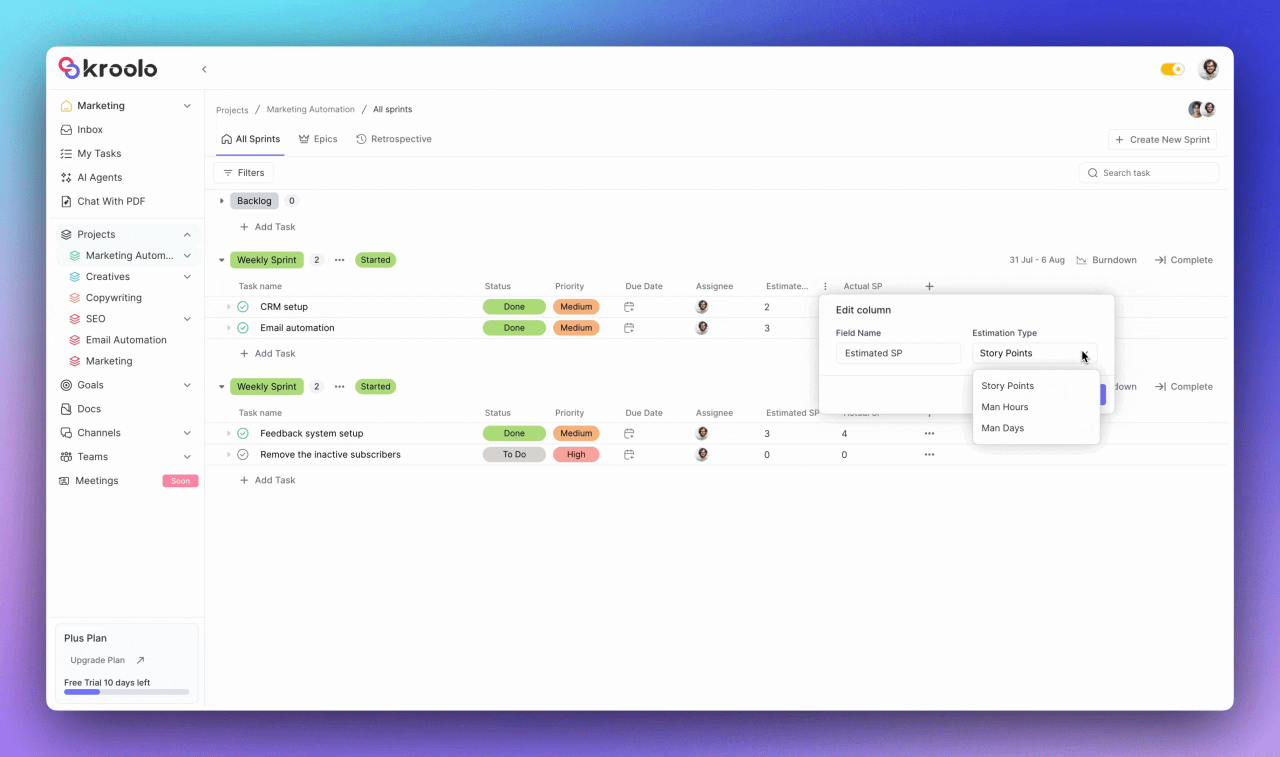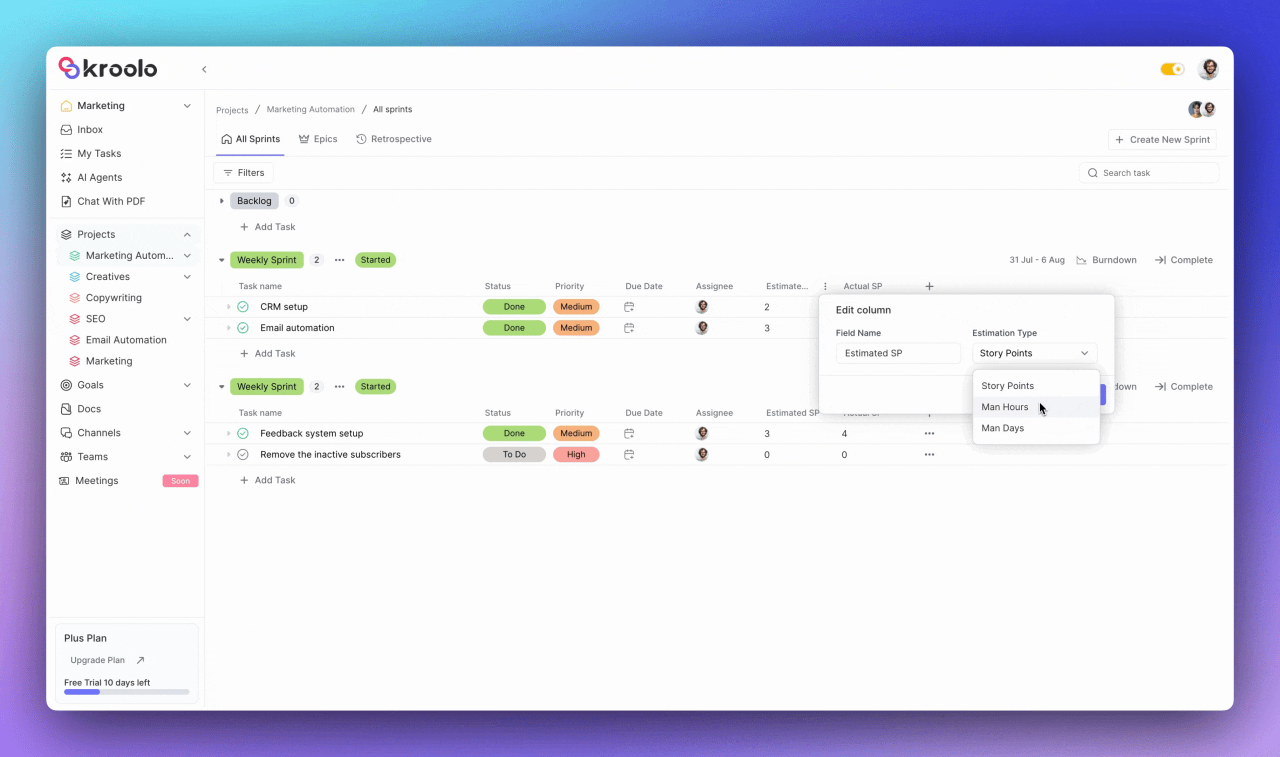
Kroolo provides sophisticated monitoring tools including burn-down charts that visualize sprint progress through estimated versus actual story points.
The blue line represents estimated points while the yellow line shows actual story points, giving teams real-time insights into their progress. These analytics help teams identify potential issues early and make data-driven adjustments to ensure sprint success.
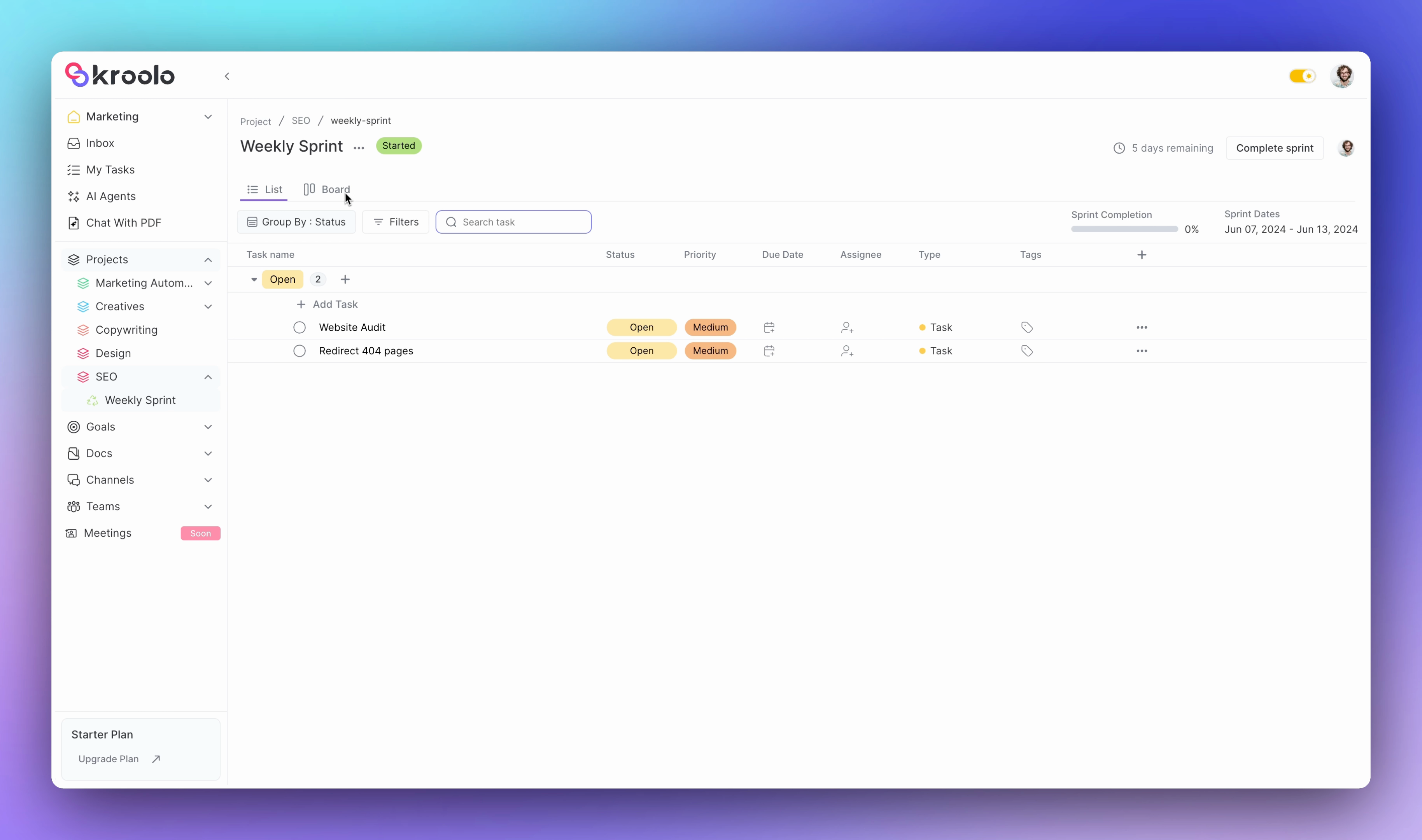
Teams can switch between different view modes including board views that organize tasks into visual groups for enhanced understanding.
The platform supports filtering, grouping, and searching capabilities that help teams locate specific tasks quickly. Collaborative features enable team members to add subtasks, mark tasks as milestones, duplicate work items, and move tasks between sprints or to the backlog as needed.
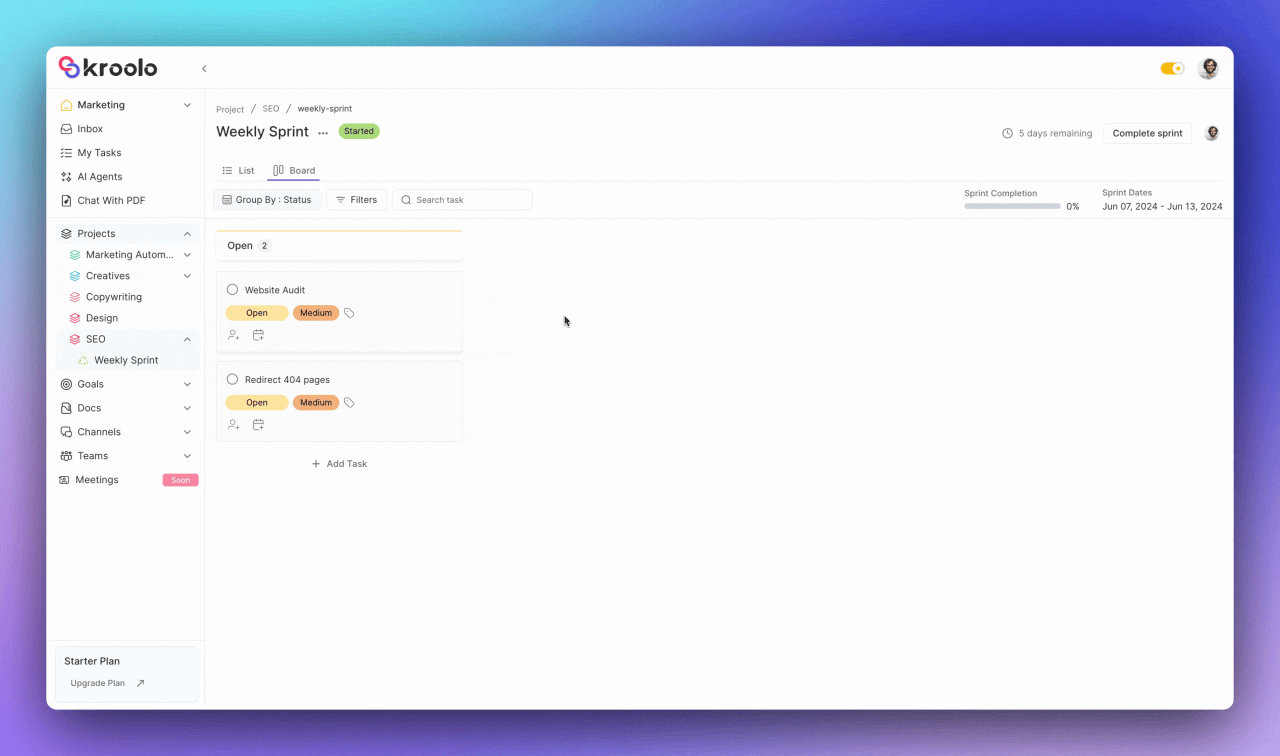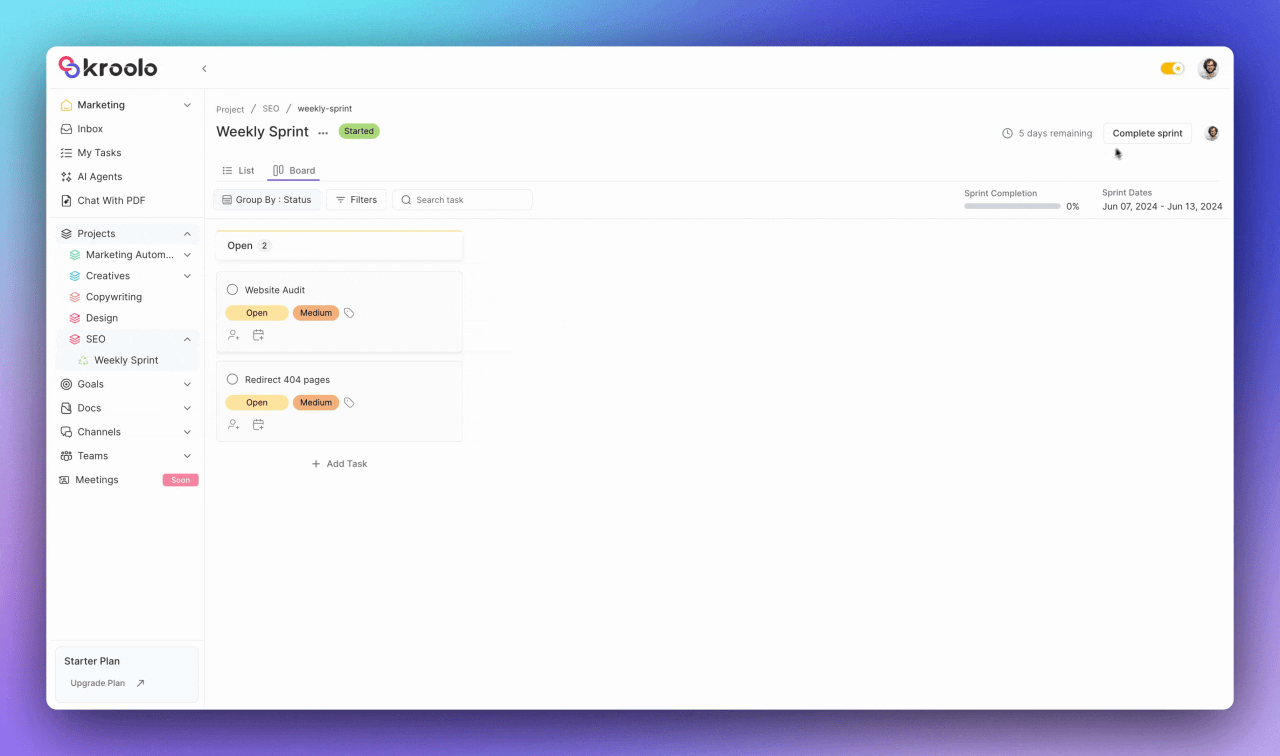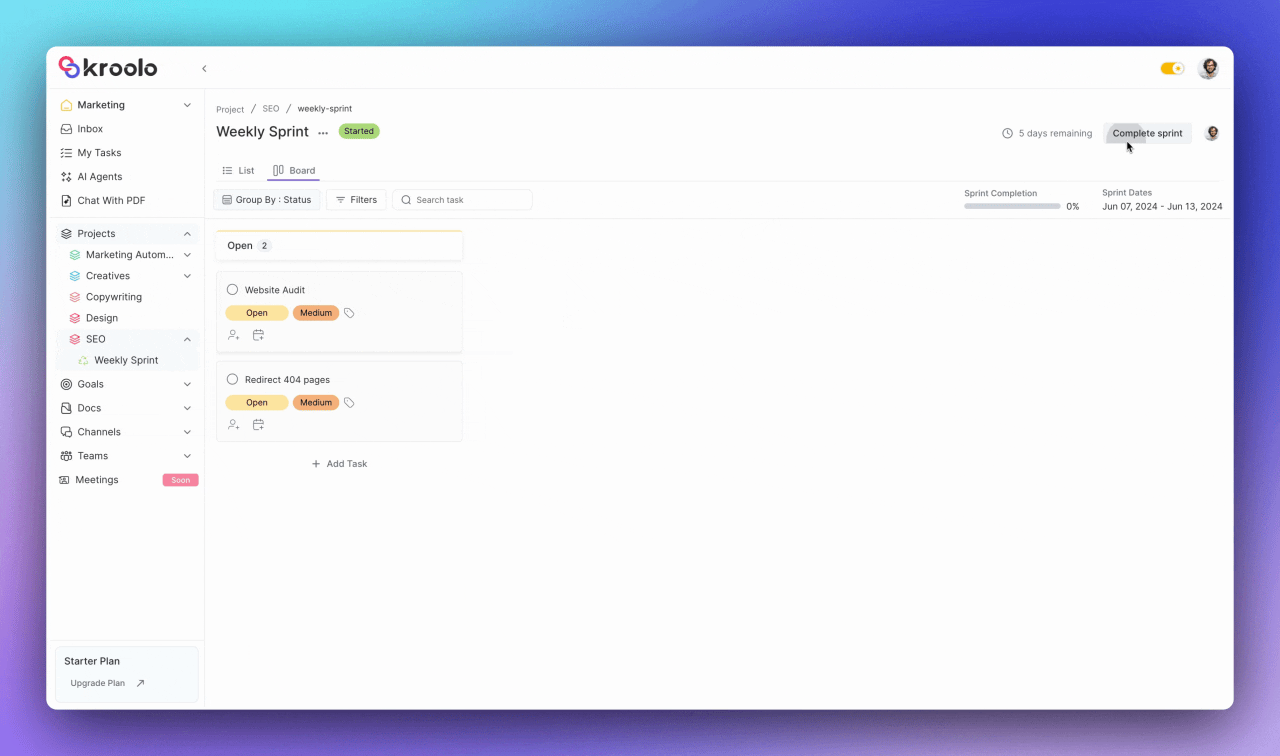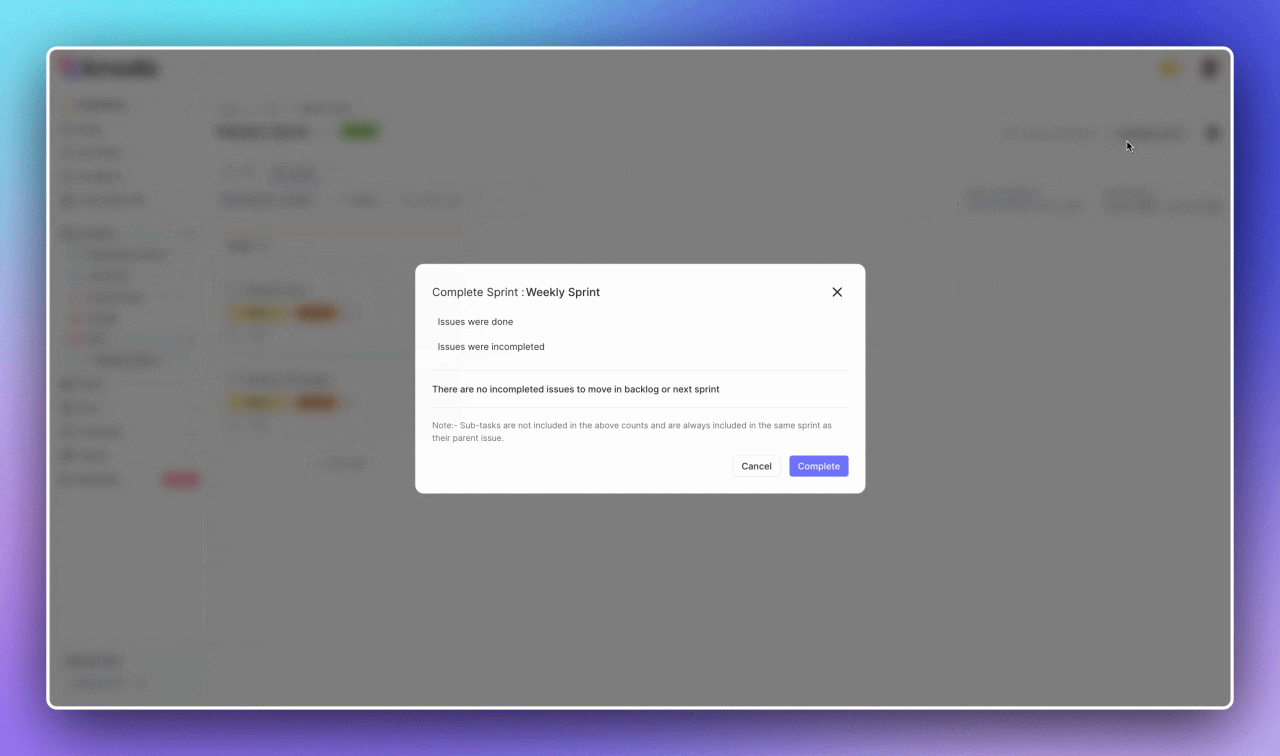
When sprints conclude, Kroolo facilitates smooth transitions through comprehensive completion workflows. Teams can handle incomplete tasks by moving them to the backlog, ensuring nothing falls through cracks.
The platform maintains historical sprint data for retrospective analysis and future planning reference, supporting continuous improvement initiatives.
Kroolo's sprint planning capabilities integrate seamlessly with broader project management functions, creating a unified environment for planning, execution, and monitoring. Teams can edit, archive, or delete sprints as needed while maintaining comprehensive audit trails.
This integration eliminates the need for multiple tools and creates a single source of truth for all project-related activities and sprint planning by Kroolo becomes a streamlined experience.
Effective sprint planning follows a structured approach that ensures teams create realistic, achievable plans while maintaining alignment with broader project objectives. These systematic steps provide a framework that teams can adapt to their specific needs while maintaining the core principles that drive successful sprint outcomes.
Before conducting sprint planning sessions, product owners must prepare and prioritize the product backlog to ensure items are ready for team consideration.
This preparation includes refining user stories, defining acceptance criteria, and estimating relative effort for backlog items. Teams should review the definition of "done" and update it based on technology, skill, or team member changes since the last sprint
The sprint planning meeting begins with establishing a clear sprint goal that provides direction and meaning for the upcoming iteration. Product owners present the overarching objective while facilitating discussion through open-ended questions.
Teams discuss any updates or changes since the last sprint retrospective that might impact current planning decisions, ensuring everyone has complete context for informed decision-making.
Teams must honestly assess their capacity for the upcoming sprint based on team member availability, competing priorities, and known constraints. Historical velocity data from previous sprints provides baseline information for realistic capacity planning.
This step includes accounting for holidays, training, meetings, and other activities that reduce available development time during the sprint period.
Teams collaboratively review prioritized product backlog items and select those that align with the sprint goal and fit within their capacity constraints.
During this process, team members ask clarifying questions, discuss technical approaches, and ensure they understand acceptance criteria. Selected items move from the product backlog into the sprint backlog, becoming the team's commitment for the iteration.
Once backlog items are selected, teams break them down into specific tasks and estimate the effort required for completion. This detailed planning helps identify potential obstacles, dependencies, and resource requirements.
Team members volunteer for specific tasks based on their skills and interests while ensuring balanced workload distribution across the team.
Teams identify potential risks, dependencies, and concerns that could impact sprint success. This includes technical dependencies, external resource requirements, and potential blockers that might arise during sprint execution. Teams document these items and develop mitigation strategies or escalation paths to address them proactively throughout the sprint cycle.
Sprint planning have become the backbone of the businesses and for successful agile management, you need to follow these best practices.
Sprint planning is not backlog grooming. Ensure that the product backlog is prioritized and that user stories are detailed, estimated (if possible), and ready for selection. This saves time and confusion during the actual sprint planning meeting.
Every sprint needs a purpose. A well-articulated sprint goal aligns the team around a common objective and helps in making prioritization decisions during the sprint.
Use historical velocity (how much the team usually completes) and available capacity (accounting for vacations, other commitments) to decide how much work the team can realistically take on.
Sprint planning isn’t just for the Product Owner or Scrum Master. It must include developers, testers, designers—everyone involved in delivery. Collective input ensures feasibility and commitment.
Avoid long-winded discussions. The rule of thumb: 2 hours of planning per 1-week sprint (i.e., max 4 hours for a 2-week sprint). Stick to it.
Use proven estimation techniques like story points and planning poker to build consensus and prevent anchoring bias. This makes the planning process collaborative and more accurate.
Once stories are selected, break them down into granular tasks (ideally 4–8 hours of effort each). This allows better tracking and helps individuals understand what needs to be done.
Make sure every selected story has a clear “Definition of Done” so there's no ambiguity about completion. This minimizes rework and ensures consistent quality.
Not every sprint is feature-rich. Make space for technical spikes, bug fixing, or unfinished stories from the last sprint. Plan accordingly so these don’t derail your commitments.
Centralize all sprint planning activities—backlog, estimates, capacity planning, task breakdown, and sprint backlog creation—within one tool. Sprint planning by Kroolo offers all of this, reducing context switching and making planning efficient, especially for remote teams.
Tags
Project Management
Productivity